Ultimate Guide to Google Search Console: Key Insights

1. Why GSC is So Useful
Google Search Console (GSC) is more than just a traffic counter. It’s a way to:
- See how Google views your site
- Understand which pages and keywords are driving traffic
- Detect and fix issues that keep pages from ranking
2. Core Metrics to Watch
When you go to Performance → Search results, focus on these:
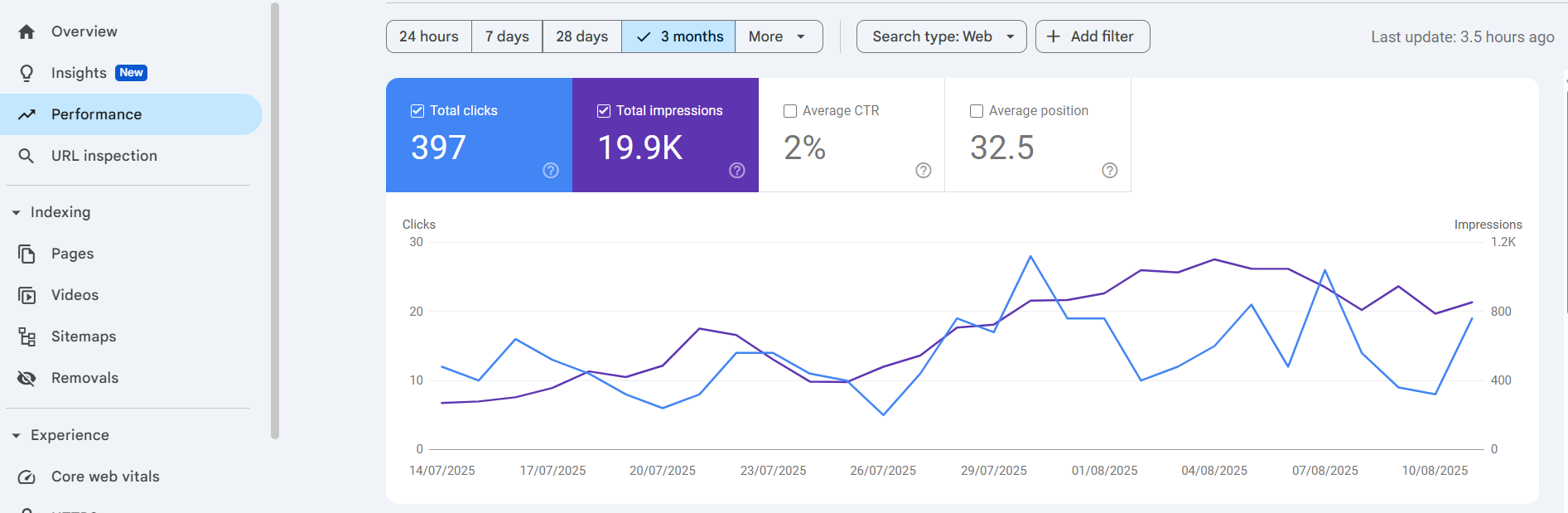
| Metric | What It Means | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Total Clicks | Times someone clicked from Google Search to your site | Shows how much traffic you’re getting |
| Total Impressions | Times your pages appeared in search results | Higher impressions can mean better visibility |
| Average CTR | % of impressions that became clicks | Low CTR could mean your title/description needs work |
| Average Position | Average ranking in search results | Closer to #1 = more clicks |
Pro Insight:
For many companies — especially SaaS — clicks and impressions follow a weekly cycle. You may see lower traffic on weekends and higher on weekdays. This is normal and should be considered when spotting trends. Always compare the same days of the week when analyzing changes.
3. Key Sections to Monitor
A. Top Pages
Go to the Pages tab in the Performance report - to see programmatic SEO results as you can see if the new pages truly get traffic.
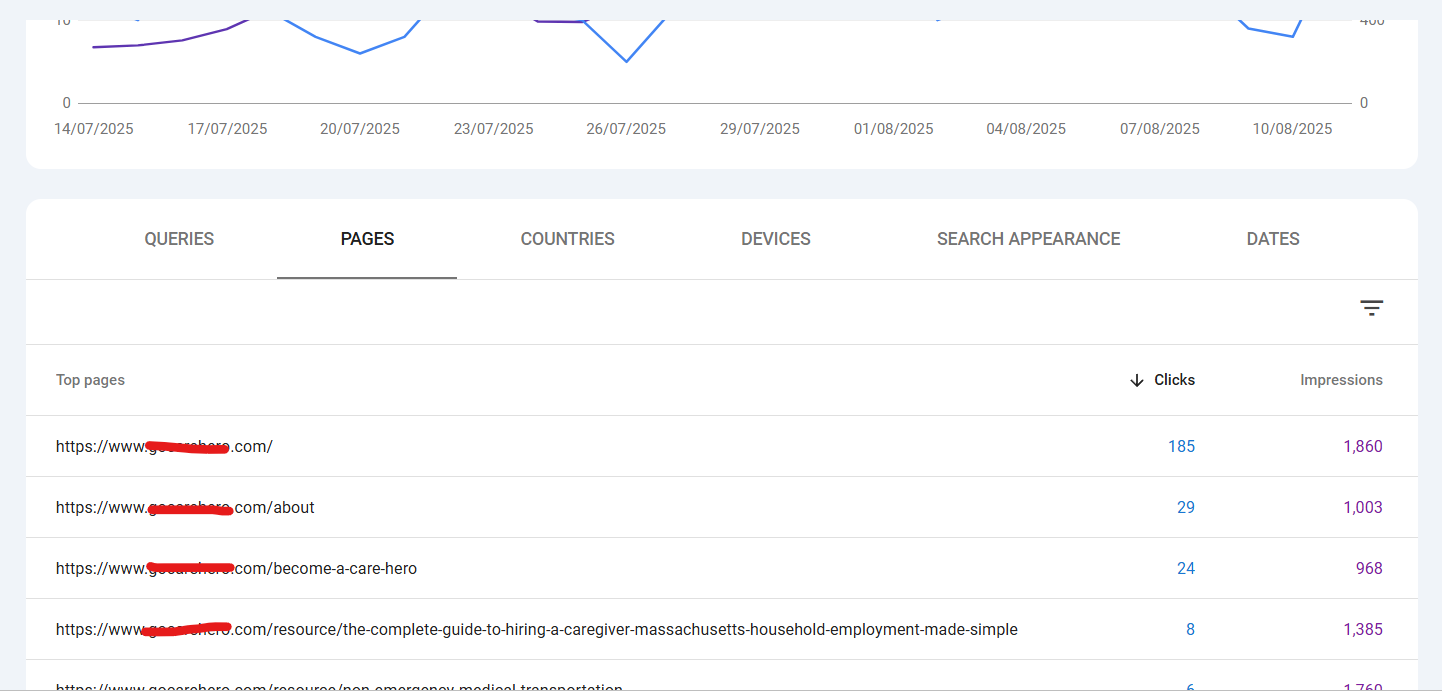
- See which pages get the most clicks and impressions.
- Look for:
- High impressions, low clicks → Improve meta titles/descriptions.
- Declining clicks → Check if rankings dropped or competition increased.
- You can filter pages that you created using programmatic SEO
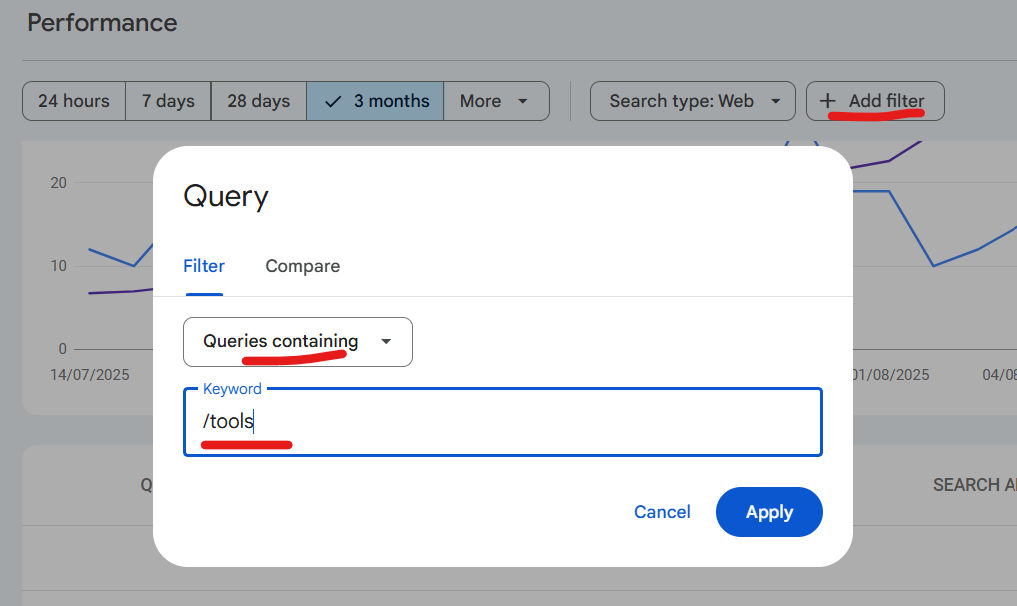
B. Search Queries
- Switch to the Queries tab.
- Identify:
- Keywords bringing the most clicks (protect these rankings).
- Keywords with high impressions but low CTR (optimize titles/descriptions).
- Keywords with rankings between positions 11–20 (optimize content to push onto page 1).
4. Index Coverage Report
This is found under Indexing → Pages. It tells you:
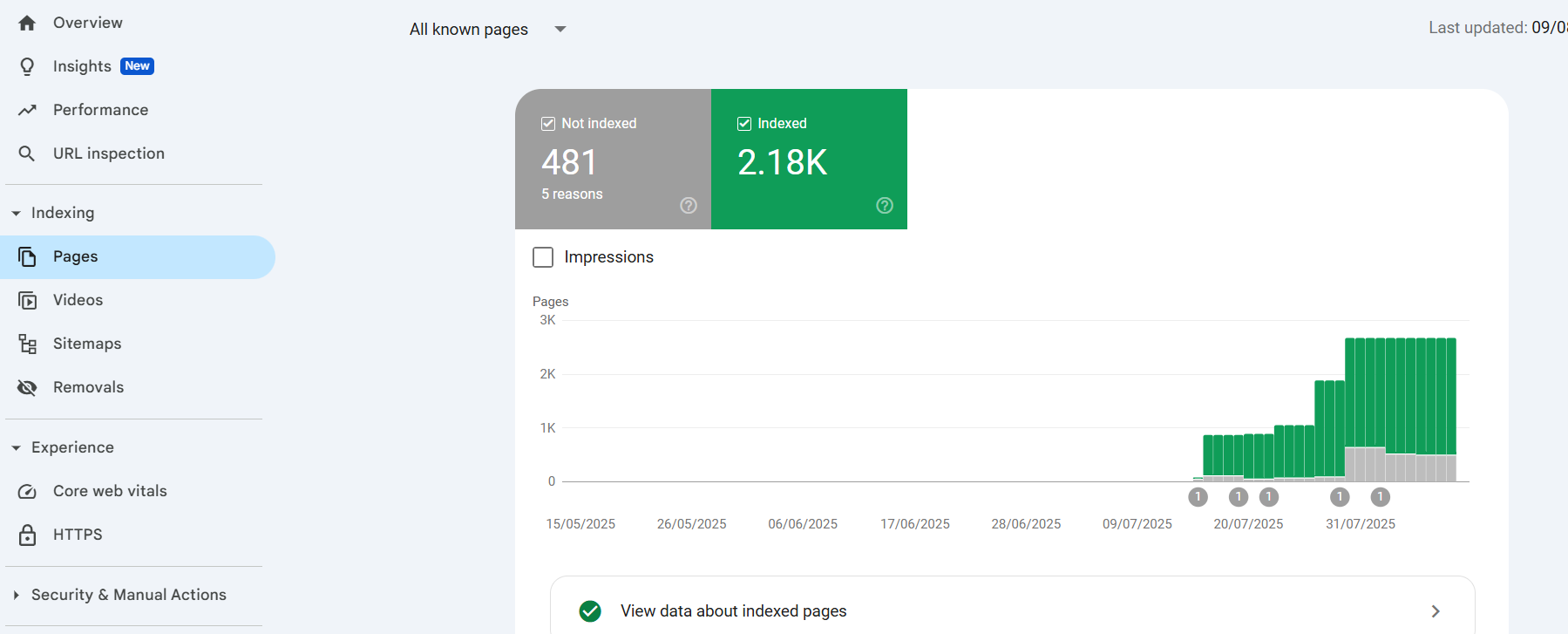
- How many of your pages are indexed (the higher the percentage, the better).
- Pages not indexed will not appear in Google Search at all.
Common Reasons Pages Aren’t Indexed:
1. Crawled – currently not indexed
What it means:
Google visited the page but decided not to index it.
Common reasons: thin content, duplicate content, or low-quality page.
How to fix:
- Add more original and valuable content to the page.
- Combine duplicate pages into one stronger page.
- Improve internal linking so the page has more authority.
- Request indexing in GSC after making changes.
2. Discovered – currently not indexed
What it means:
Google found the URL but hasn’t crawled it yet, often due to crawl budget limits or low perceived importance.
How to fix:
- Make sure the page is linked from important areas of your site (homepage, main menu, or other high-traffic pages).
- Update your sitemap in GSC so Google knows about it.
- Check server speed — slow sites can discourage crawling.
- Reduce unnecessary low-value URLs to free up crawl budget.
3. Duplicate without user-selected canonical
What it means:
Google thinks this page is a duplicate of another but you haven’t set a preferred (canonical) version.
How to fix:
- Decide which version should rank, then add a
<link rel="canonical">tag pointing to it. - Consolidate duplicate pages so you have one main version.
- Avoid creating multiple URLs for the same content.
4. Blocked by robots.txt
What it means:
Your robots.txt file tells Google not to crawl the page.
How to fix:
- Review your
/robots.txtfile atyoursite.com/robots.txt. - Remove or adjust the block if the page should be indexed.
- If you need the block for security or staging pages, keep it in place.
5. Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag
What it means:
A meta tag or HTTP header is telling Google not to index the page.
How to fix:
- Remove the
noindextag if you want the page in search results. - Make sure your CMS isn’t automatically applying
noindexto certain templates. - Only use
noindexfor truly private or low-value pages.
6. Soft 404
What it means:
The page looks like a “Not Found” page to Google but doesn’t return a proper 404 error.
How to fix:
- If the page really doesn’t exist → return a real 404 or 410 status.
- If it does exist → add useful, unique content so Google sees it as valuable.
- Check for typos in internal links that might lead to wrong URLs.
7. Server errors (5xx)
What it means:
Google couldn’t load your page because your server returned an error.
How to fix:
- Check your hosting/server logs for outages or errors.
- Improve server capacity if spikes in traffic cause downtime.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN) to reduce load and latency.
Pro Tip:
After fixing an issue, click Validate Fix in GSC for that error type. This tells Google to recheck and confirm the page is now indexable.
If you have a high percentage of non-indexed important pages, it can limit your total organic traffic potential. Always check which pages are excluded and why.
5. Tracking Over Time
- Use the Date range selector in Performance reports to compare:
- Week over week
- Month over month
- Year over year (for seasonal businesses)
- This helps spot whether changes are part of normal cycles (like weekend dips) or indicate real problems.
If you want, I can also make a visual dashboard-style cheat sheet combining:
- A weekly traffic cycle example for SaaS
- Top pages and queries breakdown
- An index coverage “health” graphic with % indexed and reasons for exclusion
That would make this instantly scannable for a beginner.



